Search
In a world where it seems best to go unnoticed, many creatures display their beauty in plain sight. We could even say that we are surrounded by beauty. A diverse
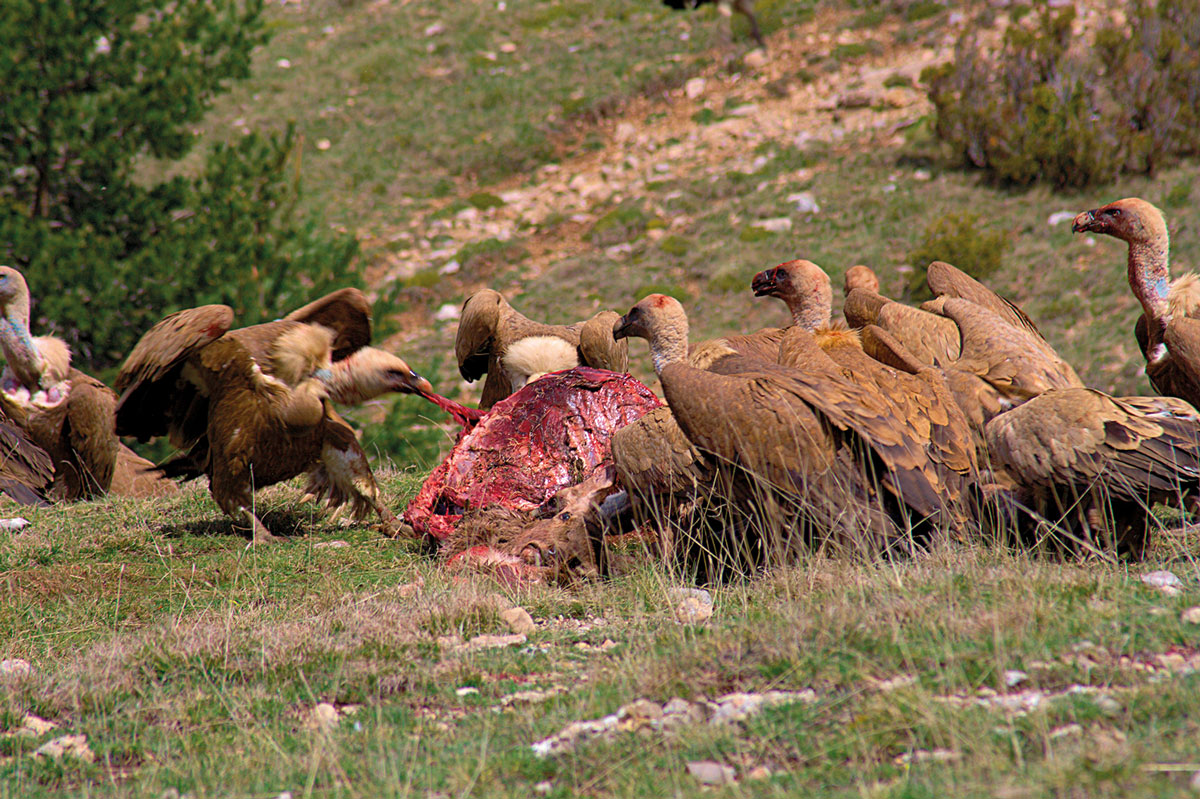
Wild animals can be environmental watchdogs that inform us about antimicrobial resistance.
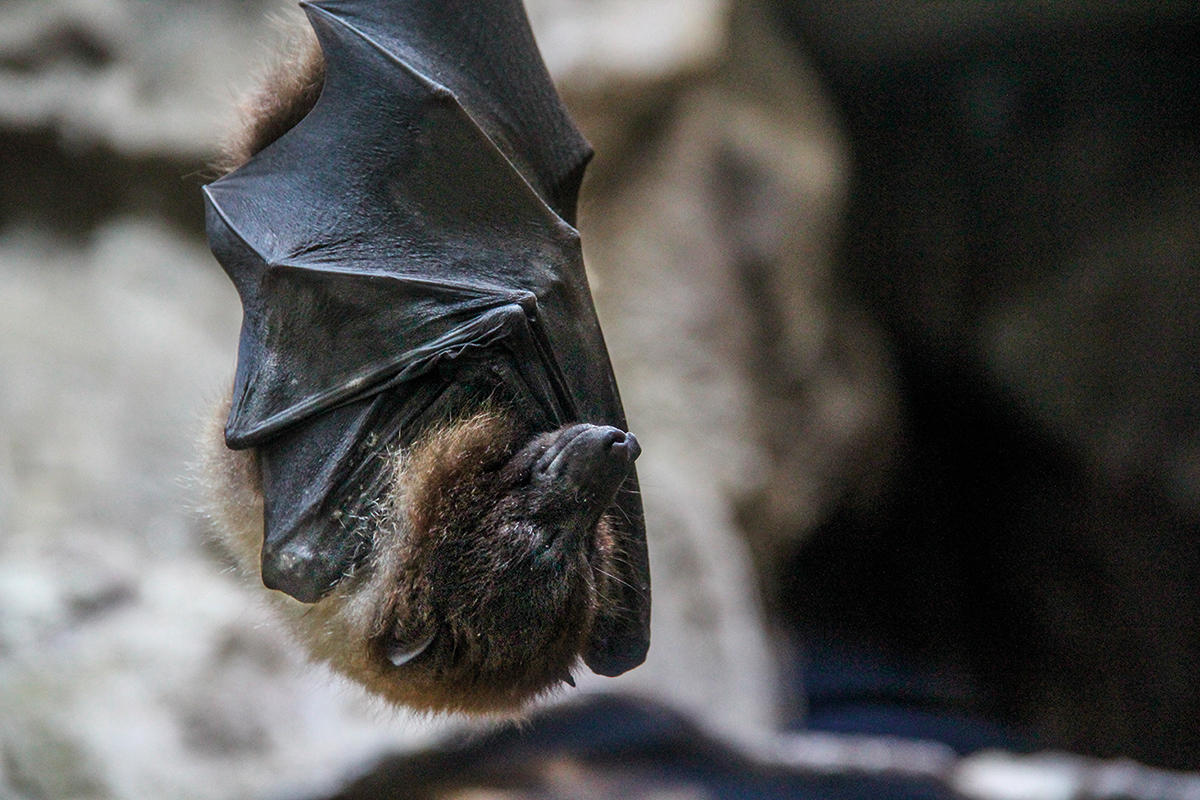
The emergence of new zoonotic diseases reminds us that humans, animals, and the environment are interconnected.
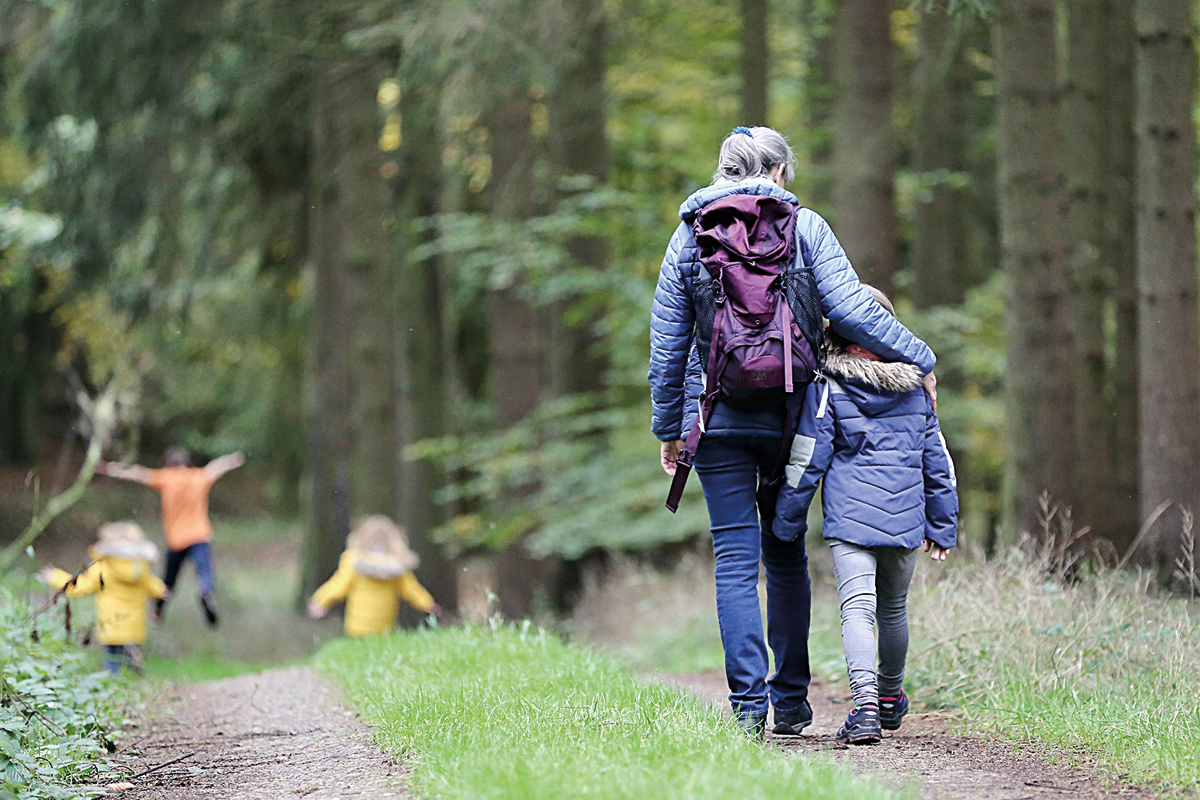
Contact with nature generates measurable benefits for people’s psychological and physiological health.
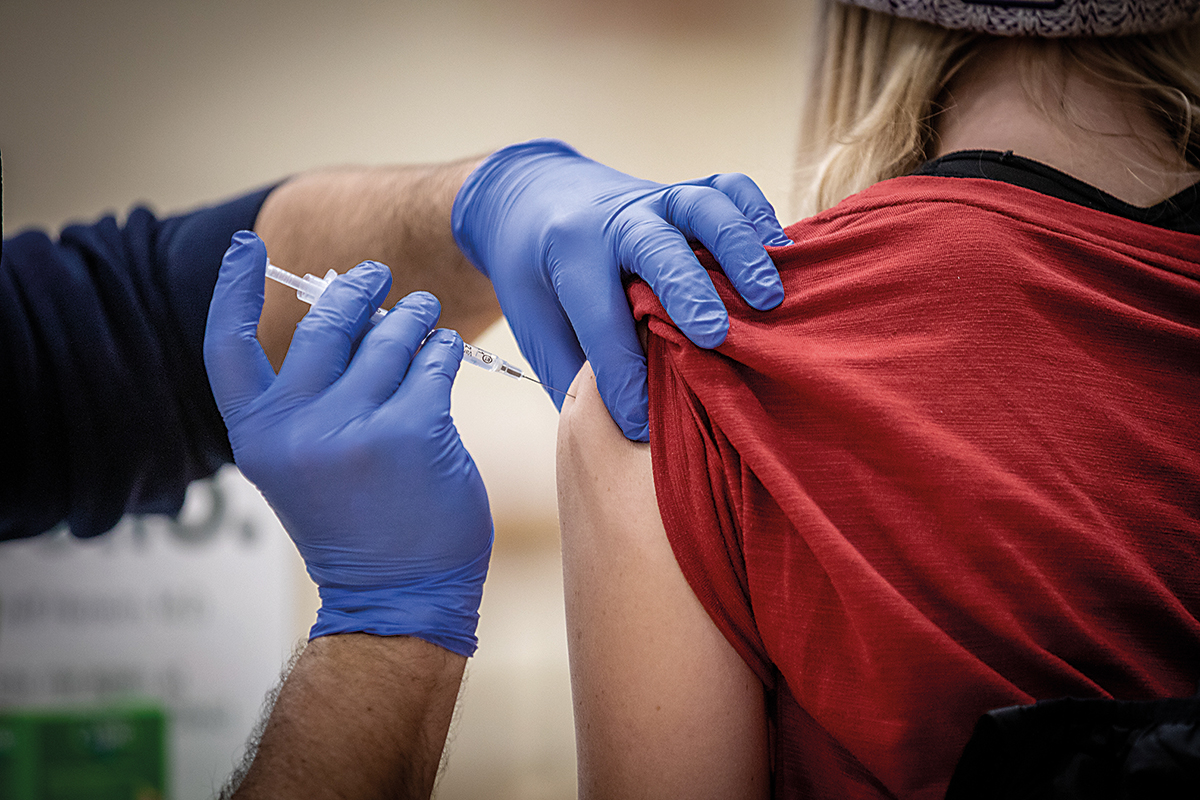
Communication research can reinforce vaccination uptake, a key public health tool, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic.
This article proposes an effort to make the most of the potential of social sciences and thus reimagine the concept of One Health.
Although a One Health perspective has, in one way or another, been around at least since the time of Hippocrates, the term itself was coined by William Karesh in a
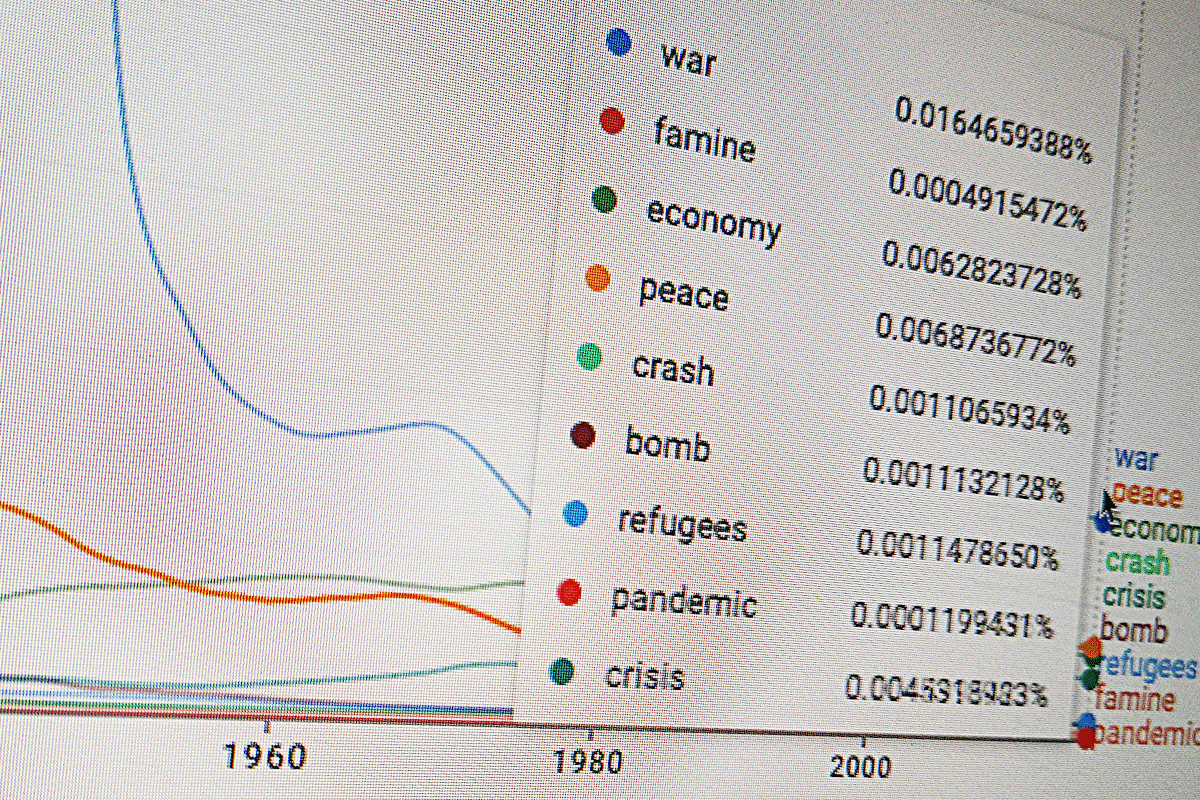
Recent advances in complex systems research, computer-based simulations, and large-scale databases, are paving the way towards fully developing a mathematical theory of human history.
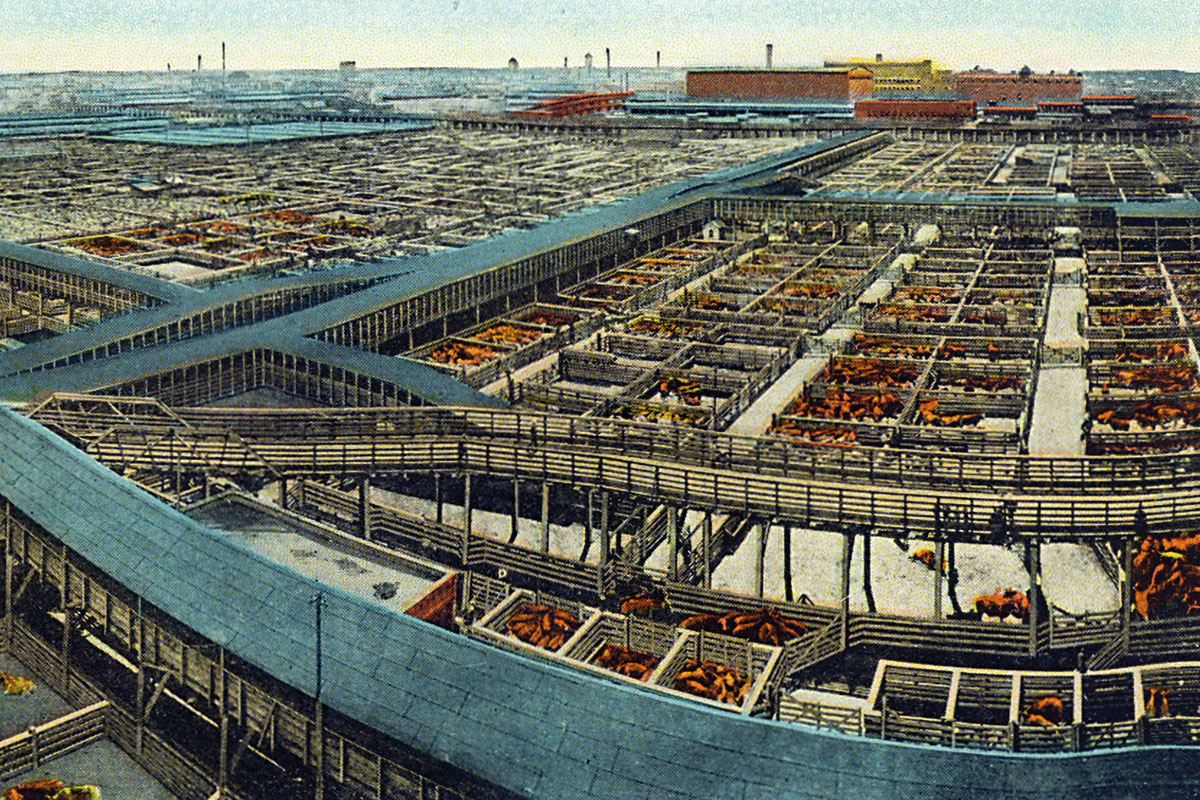
Our evolution developed a series of technical innovations such as the control of fire, agriculture and railways, which transformed not only the way we eat, but also the way we live.
What made urban experiments possible at the end of the Holocene? What selective pressures made cities more successful than other alternatives?
The most widely accepted hypothesis holds that social norms were shaped by processes of cultural selection between human groups with different rules on how to organise social life.
Much of the archaeological evidence left by humans shows the strategies they adopted in terms of mobility, the structure of exchange networks, and the evidence of their inhabiting an environment that they quickly learned to manage and appropriate.