Search
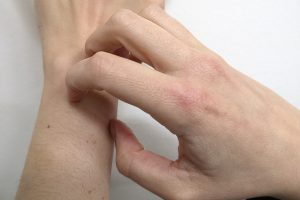
The last decade has seen a marked increase in the incidence of scabies in Spain. Esther Samper explains how this mite acts and how it affects scabies patients.
Poliomyelitis cases have increased globally in the last year. The oral polio vaccine is very effective and acts on the first line of defence.
Sickness behaviours are far from being exclusive to humans; they have been found in virtually all animals in which they have been studied.
The WHO published recommendations on how to name new infectious diseases to avoid stigmatising a country, community, or economic sector.
Nutritional epidemiology currently studies the diet-disease relationships. In this review, we analyse the impact of diet on health and the importance of dietary factors in the prevention of non-communicable diseases.
Although humans' irresponsible and indiscriminate use of the natural environment could be one of the causes behind the recent coronavirus crisis, bats have been targeted for their role as natural reservoirs of zoonotic pathogens.
An epidemic like the one we have unfortunately experienced can bring out people's worst fears. Cinema and literature have successfully used fear to write scripts in which an epidemic is the heart of the story or the underlying excuse.
Maurice Hilleman is probably the scientist who has prevented the highest number of deaths and illnesses from infection in the history of medicine. He and his team obtained or improved more than 25 vaccines against viruses and bacteria.
Although the coronavirus is a microbe, the author uses two animal analogies to explain the sudden and unexpected (or otherwise) appearance of phenomena such as COVID-19, but also other «unexpected» disasters of an economic, social, or political nature.