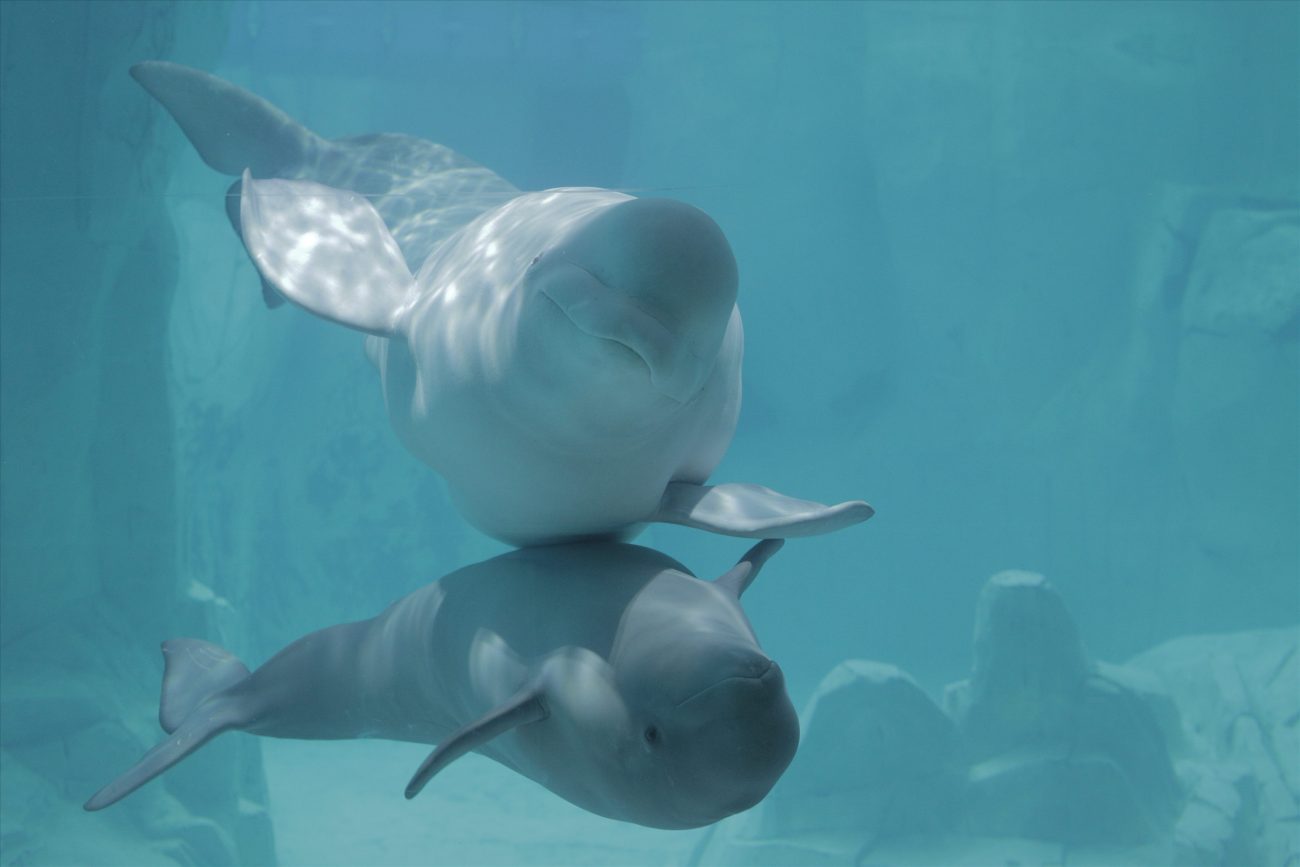
What we think of as underwater «melodies» are actually the set of sounds that constitute the communication system of whales and other cetaceans such as dolphins or belugas. Some species, such as the humpback whales, use sounds to communicate, navigate, and hunt that resemble human songs. This is why we call the sounds of many of these cetacean sounds songs.
All cetaceans, including whales and dolphins, are highly dependent on acoustic communication, since other senses such as smell and vision – used extensively by land mammals – are reduced for them in the aquatic environment. This is why they are intensely vocal animals and have a highly evolved sense of hearing. Also, did you know that the sounds some whales produce can travel up to 3,000 kilometers across the ocean?
Answered by Paola Muñoz, biologist working at the Oceanographic Museum and member of the team of caretakers that look after beluga whales and other marine mammals at the centre.
Question submitted by Nuria Carrasco.
«Mètode’s whys and wherefores» is a science consultation office where the readers send their scientific questions and an expert answers them. You can send your question using this form. All the questions we receive until 15 June will participate in a draw to win a selection of Mètode publications.
* The draw might be postponed due to the health care crisis.